Merlin
(Genus, species: Falco columbarius)
The merlin is a fairly small raptor that used to be called the Pigeon Hawk. They look a bit like pigeons when they're flying.
There are slightly different sub-species of Merlin. The Tundra Merlin (for example) tends to be darker in color than the Prairie Merlin. They are all considered the same species, however.
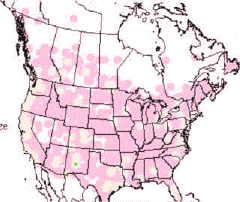
General: The Merlin is distributed widely throughout North America but is not particularly common anywhere. This is mainly because they are territorial birds who need large hunting areas to sustain themselves and their offspring.

female merlin
Description - male: Merlins are small for a bird of prey, 10 to 13 inches long with a wingspan of 24 to 27 inches.
The breast and belly of the Merlin are buff (tan) with dark brown streaks. The throat is white. The upperparts (back, wings and tail), eyeline and crown of the Merlin are light blue-gray. The head of the Merlin is a buff (tan) color) with fine dark streaks and a distinct tan eyebrow. The tail is narrow and banded and the wings are pointed. The legs and feet are yellow with black talons. The beak is a blue-gray color with yellow toward the head. The eyes are brown.
Description - female: The coloring and size of the female Merlin is the same as the male, but instead of blue-gray coloring on the back, wings, tail and crown, the female Merlin is brown.
Description - young: Immature Merlins look much like the females. When hatched, the young are covered in down. They begin to get quill feathers after 14 days and all but the head is covered by feathers by the time they are 18 days old. About three to four weeks after hatching, the nestlings are ready for flight.

swallow
Feeding: The Merlin's main prey (about 80% of their diet) is smaller birds (finches, sparrows, waxwings, swallows, etc) which it catches in flight. They also eat some large insects (like dragonflies), small mammals, lizards and snakes.
Habitat: Breeding occurs in forested or suburban areas. During other times of the year, they prefer open areas and can be found in fields, grasslands, marshlands, deserts, seashores and lakeshores.
Nesting: They mainly nest in trees, crevices or cliffs. They often reuse the abandoned nests of other raptors, crows, jays or magpies lining the borrowed nest with fresh vegetation.
The female typically lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs. The eggs are a creamy white color and are blotched with chocolate, brown and purple markings. The eggs are not laid all at once -- instead the female waits about 2 days between each.
Both parents incubate the eggs, which takes about one month, though the female does most of the work.